Yarn cluster 模式运行机制源码分析
启动下面的代码:
bin/spark-submit \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.1.1.jar \
100
yarn 会按照下面的顺序依次启动了 3 个进程:
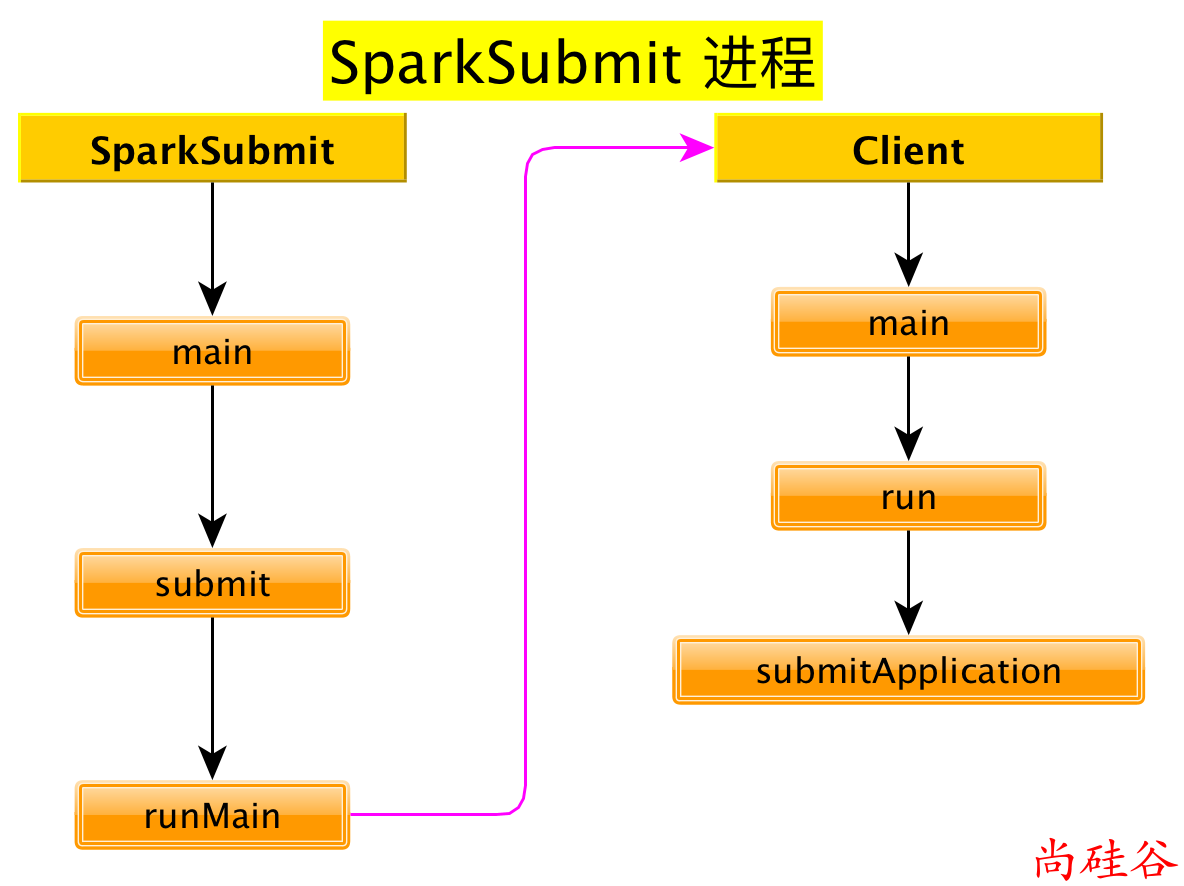
SparkSubmit
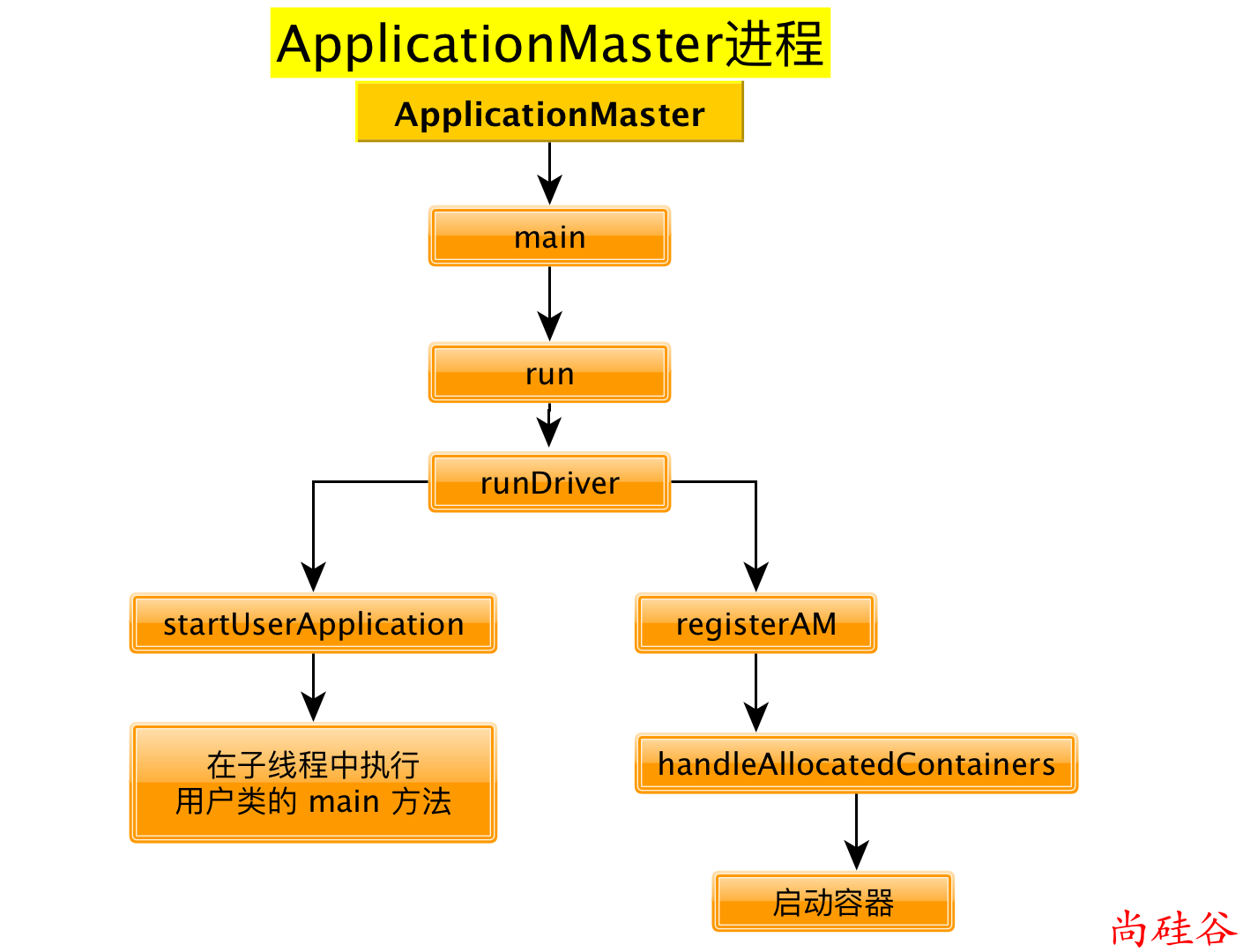
ApplicationMaster
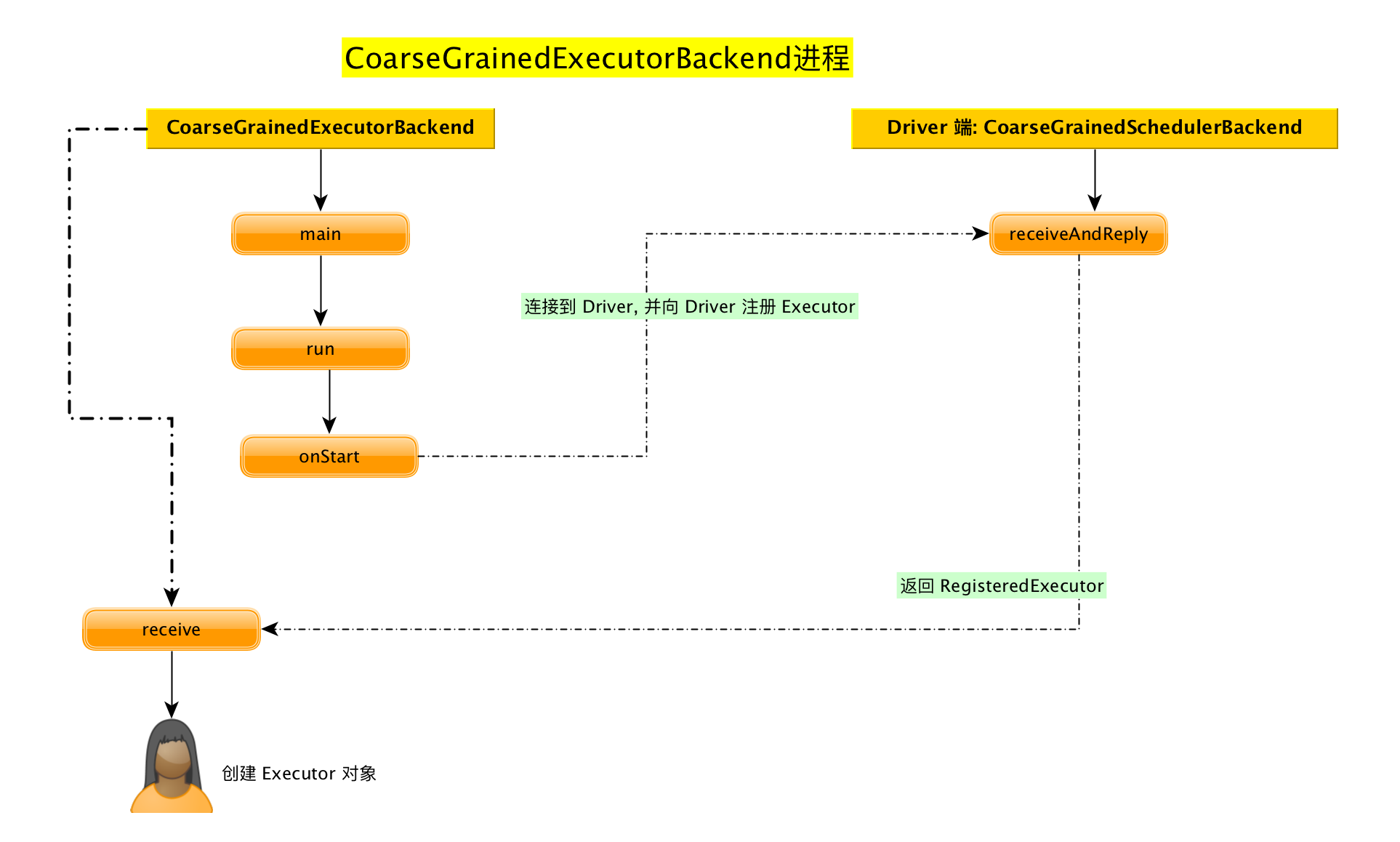
CoarseGrainedExecutorB ackend
1. bin/spark-submit 启动脚本分析
启动类org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
/bin/spark-class
exec "${CMD[@]}"
最终启动类:
/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_172/bin/java
-cp /opt/module/spark-yarn/conf/:/opt/module/spark-yarn/jars/*:/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2/etc/hadoop/
org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit
--master yarn
--deploy-mode cluster
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.1.1.jar 100
2. org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit 源码分析
SparkSubmit伴生对象
main方法
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/*
参数
--master yarn
--deploy-mode cluster
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.1.1.jar 100
*/
val appArgs = new SparkSubmitArguments(args)
appArgs.action match {
// 如果没有指定 action, 则 action 的默认值是: action = Option(action).getOrElse(SUBMIT)
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)
}
}
submit方法
/**
* 使用提供的参数提交应用程序
* 有 2 步:
* 1. 准备启动环境.
* 根据集群管理器和部署模式为 child main class 设置正确的 classpath, 系统属性,应用参数
* 2. 使用启动环境调用 child main class 的 main 方法
*/
@tailrec
private def submit(args: SparkSubmitArguments): Unit = {
// 准备提交环境 childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client"
val (childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
def doRunMain(): Unit = {
if (args.proxyUser != null) {
} else {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
}
if (args.isStandaloneCluster && args.useRest) {
// 在其他任何模式, 仅仅运行准备好的主类
} else {
doRunMain()
}
}
prepareSubmitEnvironment方法
// In yarn-cluster mode, use yarn.Client as a wrapper around the user class
if (isYarnCluster) {
// 在 yarn 集群模式下, 使用 yarn.Client 来封装一下 user class
childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client"
}
doRunMain方法
def doRunMain(): Unit = {
if (args.proxyUser != null) {
} else {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sysProps, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
}
runMain方法
/**
*
* 使用给定启动环境运行 child class 的 main 方法
* 注意: 如果使用了cluster deploy mode, 主类并不是用户提供
*/
private def runMain(
childArgs: Seq[String],
childClasspath: Seq[String],
sysProps: Map[String, String],
childMainClass: String,
verbose: Boolean): Unit = {
var mainClass: Class[_] = null
try {
// 使用反射的方式加载 childMainClass = "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client"
mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)
} catch {
}
// 反射出来 Client 的 main 方法
val mainMethod = mainClass.getMethod("main", new Array[String](0).getClass)
if (!Modifier.isStatic(mainMethod.getModifiers)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("The main method in the given main class must be static")
}
try {
// 调用 main 方法.
mainMethod.invoke(null, childArgs.toArray)
} catch {
}
}
3. org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client 源码分析
main方法
def main(argStrings: Array[String]) {
// 设置环境变量 SPARK_YARN_MODE 表示运行在 YARN mode
// 注意: 任何带有 SPARK_ 前缀的环境变量都会分发到所有的进程, 也包括远程进程
System.setProperty("SPARK_YARN_MODE", "true")
val sparkConf = new SparkConf
// 对传递来的参数进一步封装
val args = new ClientArguments(argStrings)
new Client(args, sparkConf).run()
}
Client.run方法
def run(): Unit = {
// 提交应用, 返回应用的 id
this.appId = submitApplication()
}
client.submitApplication方法
/**
*
* 向 ResourceManager 提交运行 ApplicationMaster 的应用程序。
*
*/
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {
var appId: ApplicationId = null
try {
// 初始化 yarn 客户端
yarnClient.init(yarnConf)
// 启动 yarn 客户端
yarnClient.start()
// 从 RM 创建一个应用程序
val newApp = yarnClient.createApplication()
val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse()
// 获取到 applicationID
appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId()
reportLauncherState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED)
launcherBackend.setAppId(appId.toString)
// Set up the appropriate contexts to launch our AM
// 设置正确的上下文对象来启动 ApplicationMaster
val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)
// 创建应用程序提交任务上下文
val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext)
// 提交应用给 ResourceManager 启动 ApplicationMaster
// "org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster"
yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext)
appId
} catch {
}
}
方法:
createContainerLaunchContext
private def createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse: GetNewApplicationResponse)
: ContainerLaunchContext = {
val amClass =
if (isClusterMode) { // 如果是 Cluster 模式
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster").getName
} else { // 如果是 Client 模式
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher").getName
}
amContainer
}
至此, SparkSubmit 进程启动完毕.
4. org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster 源码分析
ApplicationMaster伴生对象的main方法
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
SignalUtils.registerLogger(log)
// 构建 ApplicationMasterArguments 对象, 对传来的参数做封装
val amArgs: ApplicationMasterArguments = new ApplicationMasterArguments(args)
SparkHadoopUtil.get.runAsSparkUser { () =>
// 构建 ApplicationMaster 实例 ApplicationMaster 需要与 RM通讯
master = new ApplicationMaster(amArgs, new YarnRMClient)
// 运行 ApplicationMaster 的 run 方法, run 方法结束之后, 结束 ApplicationMaster 进程
System.exit(master.run())
}
}
ApplicationMaster伴生类的run方法
final def run(): Int = {
// 关键核心代码
try {
val fs = FileSystem.get(yarnConf)
if (isClusterMode) {
runDriver(securityMgr)
} else {
runExecutorLauncher(securityMgr)
}
} catch {
}
exitCode
}
runDriver方法
private def runDriver(securityMgr: SecurityManager): Unit = {
addAmIpFilter()
// 开始执行用户类. 启动一个子线程来执行用户类的 main 方法. 返回值就是运行用户类的子线程.
// 线程名就叫 "Driver"
userClassThread = startUserApplication()
val totalWaitTime = sparkConf.get(AM_MAX_WAIT_TIME)
try {
// 注册 ApplicationMaster , 其实就是请求资源
registerAM(sc.getConf, rpcEnv, driverRef, sc.ui.map(_.appUIAddress).getOrElse(""),
securityMgr)
// 线程 join: 把userClassThread线程执行完毕之后再继续执行当前线程.
userClassThread.join()
} catch {
}
}
startUserApplication方法
private def startUserApplication(): Thread = {
// 得到用户类的 main 方法
val mainMethod = userClassLoader.loadClass(args.userClass)
.getMethod("main", classOf[Array[String]])
// 创建及线程
val userThread = new Thread {
override def run() {
try {
// 调用用户类的主函数
mainMethod.invoke(null, userArgs.toArray)
} catch {
} finally {
}
}
}
userThread.setContextClassLoader(userClassLoader)
userThread.setName("Driver")
userThread.start()
userThread
}
registerAM方法
private def registerAM(
_sparkConf: SparkConf,
_rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
driverRef: RpcEndpointRef,
uiAddress: String,
securityMgr: SecurityManager) = {
// 向 RM 注册, 得到 YarnAllocator
allocator = client.register(driverUrl,
driverRef,
yarnConf,
_sparkConf,
uiAddress,
historyAddress,
securityMgr,
localResources)
// 请求分配资源
allocator.allocateResources()
}
allocator.allocateResources()方法
/**
请求资源,如果 Yarn 满足了我们的所有要求,我们就会得到一些容器(数量: maxExecutors)。
通过在这些容器中启动 Executor 来处理 YARN 授予我们的任何容器。
必须同步,因为在此方法中读取的变量会被其他方法更改。
*/
def allocateResources(): Unit = synchronized {
if (allocatedContainers.size > 0) {
handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala)
}
}
handleAllocatedContainers方法
/**
处理 RM 授权给我们的容器
*/
def handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers: Seq[Container]): Unit = {
val containersToUse = new ArrayBuffer[Container](allocatedContainers.size)
runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse)
}
runAllocatedContainers方法
/**
* Launches executors in the allocated containers.
在已经分配的容器中启动 Executors
*/
private def runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse: ArrayBuffer[Container]): Unit = {
// 每个容器上启动一个 Executor
for (container <- containersToUse) {
if (numExecutorsRunning < targetNumExecutors) {
if (launchContainers) {
launcherPool.execute(new Runnable {
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
new ExecutorRunnable(
Some(container),
conf,
sparkConf,
driverUrl,
executorId,
executorHostname,
executorMemory,
executorCores,
appAttemptId.getApplicationId.toString,
securityMgr,
localResources
).run() // 启动 executor
updateInternalState()
} catch {
}
}
})
} else {
}
} else {
}
}
}
ExecutorRunnable.run方法
def run(): Unit = {
logDebug("Starting Executor Container")
// 创建 NodeManager 客户端
nmClient = NMClient.createNMClient()
// 初始化 NodeManager 客户端
nmClient.init(conf)
// 启动 NodeManager 客户端
nmClient.start()
// 启动容器
startContainer()
}
ExecutorRunnable.startContainer()
def startContainer(): java.util.Map[String, ByteBuffer] = {
val ctx = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext])
.asInstanceOf[ContainerLaunchContext]
// 准备要执行的命令
val commands = prepareCommand()
ctx.setCommands(commands.asJava)
// Send the start request to the ContainerManager
try {
// 启动容器
nmClient.startContainer(container.get, ctx)
} catch {
}
}
ExecutorRunnable.prepareCommand方法
private def prepareCommand(): List[String] = {
val commands = prefixEnv ++ Seq(
YarnSparkHadoopUtil.expandEnvironment(Environment.JAVA_HOME) + "/bin/java",
"-server") ++
javaOpts ++
// 要执行的类
Seq("org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend",
"--driver-url", masterAddress,
"--executor-id", executorId,
"--hostname", hostname,
"--cores", executorCores.toString,
"--app-id", appId) ++
userClassPath ++
Seq(
s"1>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stdout",
s"2>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stderr")
commands.map(s => if (s == null) "null" else s).toList
}
至此, ApplicationMaster 进程启动完毕
5. org.apache.spark.executor.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 源码分析
CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 伴生对象
main方法
def main(args: Array[String]) {
// 启动 CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
run(driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, appId, workerUrl, userClassPath)
// 运行结束之后退出进程
System.exit(0)
}
run方法
/**
准备 RpcEnv
*/
private def run(
driverUrl: String,
executorId: String,
hostname: String,
cores: Int,
appId: String,
workerUrl: Option[String],
userClassPath: Seq[URL]) {
SparkHadoopUtil.get.runAsSparkUser { () =>
val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(
driverConf, executorId, hostname, port, cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", new CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(
env.rpcEnv, driverUrl, executorId, hostname, cores, userClassPath, env))
}
}
CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend 伴生类
继承自: ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint 是一个RpcEndpoint
查看生命周期方法
onStart方法
连接到 Driver, 并向 Driver注册Executor
override def onStart() {
rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>
// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"
driver = Some(ref)
// 向驱动注册 Executor 关键方法
ref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls))
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {
case Success(msg) =>
case Failure(e) =>
// 注册失败, 退出 executor
exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)
}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)
}
Driver端的CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend的receiveAndReply方法
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
// 接收注册 Executor
case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls) =>
if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) { // 已经注册过了
} else {
// 给 Executor 发送注册成功的信息
executorRef.send(RegisteredExecutor)
}
}
Eexcutor端的CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend的receive方法
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {
// 向 Driver 注册成功
case RegisteredExecutor =>
logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")
try {
// 创建 Executor 对象 注意: Executor 其实是一个对象
executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false)
} catch {
}
}
至此, Executor 创建完毕
总结